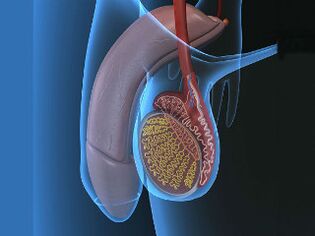
The testes are a pair of organs located in the skin sac, isolated from each other. It produces sperm and testosterone. Also, it produces sperm. Therefore, the testes are the reproductive organs of every human being.
Each egg is covered with a shell, usually one smaller than the other. Their slight asymmetry is not a pathology, but a general phenomenon.
They enter the scrotum shortly before birth. They are shaped like ellipses that are 5 cm long and 3. 5 cm wide. The average weight of a testicle is 15 to 25 grams, and it turns out that their size directly depends on the place of residence and ethnicity. The scrotum protects the testicles from injury and extreme temperatures. Her skin is very sensitive, as is her entire organ. Therefore, even mild pain in the testicles can affect the state of the entire body: mild nausea, nervousness, dizziness, etc.
Sometimes a question pops up as to why a man's egg is hurting, and the cause of this symptom can vary. Pain can have different characteristics: pain, pulling, throbbing, shooting. Most of the time, one cannot tell what the reason is. Unpleasant and painful feelings should not be ignored under any circumstances.
You need an urgent appointment. Urologists work to determine what causes certain types of pain. The doctor will examine and feel the testicles to determine if there is any inflammatory disease: swelling, internal sealing, signs of pain. A full inspection will be carried out if necessary.
Symptoms that indicate a problem with the testicles:
- presence of seals or small tumors;
- Pain on palpation or changes in shape and size;
- the presence of pain not caused by any injury;
- Pain that lasts more than an hour after injury to the testicle;
- Presence of pulling, exacerbated pain;
- temperature rises.
Next, we'll take a closer look at why a man's egg hurts -- what causes pain.
Injuried. When the cause of the pain is an injury due to mechanical shock. Its duration and intensity are proportional to the severity of the impact. Small bruises can cause severe short-term pain.
Severe pain from a serious injury can cause shock or cause loss of consciousness. If there is discomfort in the testicles, pay attention to the type of pain. If it doesn't go away and gets worse for a long time, then we can assume that there is chronic damage. Cuts and stab wounds are especially dangerous. In this case, an ambulance is required, otherwise there is a high risk of losing the testicles.
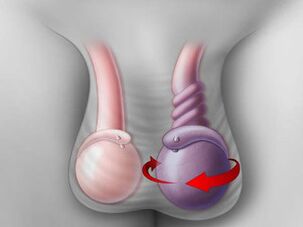
distortion. It's unclear why this happens, but the consequences of this phenomenon are so severe that it can even lead to the death of the testicles. Acute pain occurs suddenly when twisting.
Blood circulation stops and the vas deferens is compressed. In this case, you should seek medical attention immediately, no later than 7 hours later. Typically, manual twisting is done first. If that doesn't help, then they resort to surgical intervention. In most cases, this phenomenon occurs at a young age.
inflammation. It can be inside the epididymis (epididymitis) and the testis itself (orchitis). The causes of these diseases are viral and bacterial infections that are spread during sexual intercourse.
Epididymitis is characterized by increased pain on one side, swelling of the scrotum, pain and burning with urination, discharge of white fluid from the urethra, increased body temperature, and possible blood in the semen.
Etiology: prostatitis, urethritis, urinary tract infection, tuberculosis complications. May be acute and chronic. The initial phase lasts up to a month and a half. Inability to conceive will be a complication and the result of untreated.
Chronic epididymitis can be talked about if you have been ill for more than six months. It is accompanied by a deterioration of overall health, weakened immune system, and inflammation into the skin sacs. With orchitis, the testicles increase, causing pain. Sharp rise in temperature, pain in groin and lower back.
The skin sac becomes smooth due to the blood spillage. Pain increases with walking or exertion. This phenomenon may be the result of trauma or contact with the patient (mumps, typhoid, stumbling).
Unsatisfactory sexual arousal. It can also cause pain. Prolonged erections can cause blood to stagnate. Most of the time, it goes away on its own and doesn't require any treatment.
hernia. The organ passes from the peritoneum through the hole formed into the skin sac. Visually looks like a bump in the groin or scrotum. Cause pain, especially to palpation. When they increase, nausea and vomiting occur. It can be said to violate the hernia. If surgery is not performed, peritonitis necrosis may occur.
You can talk about prostatitis if you have:
- You feel a strong burning sensation when you urinate;
- Increased frequency of urination at night;
- persistent urge and feeling of fullness;
- the presence of pain during ejaculation;
- The tip of the penis is the source of pain.
Renal colic. Because of urolithiasis, stones move along the urinary tract. The pain is so intense that it radiates into the scrotum. This usually causes nausea and vomiting.
Varicose veins. In this disease, the veins in the skin sac dilate, and a lump develops around the egg and increases in size. It does not pose a threat to a person's health and does not cause much concern in his lifetime. But with complications, it can lead to infertility. Usually observed on the left side (80-98%). This is because veins from different sides flow in different ways.
Bilateral varicoceles are only observed in 2-12% of cases and on the right side in 3-8%. The cause of this disease is the poor functioning of the valves located in the blood vessels. Through hard work or exercise, as well as a standing position, this can lead to increased boating. This is how the veins around the spermatic cord swell. Features of the anatomical location of the renal veins and superior arteries can also contribute to this disease.

edema. In the shell of the testis, a buildup of serous fluid occurs.
The result can be injury, heart failure, and damage to lymph nodes in the groin or pelvis.
The skin sacs increase and pain occurs. It is diagnosed by simple detection and, in special cases, requires ultrasound. removed during surgery.
sperm cyst. In the testis, an empty sac forms, fills with sperm fluid, and does not reach significant size. The leather bag is not deformed and is not accompanied by pain. May be emptied during ejaculation.
tumor. Testicular pain can lead to malignancy. Cryptorchidism can cause this pathology. The disease occurs when the testicles do not descend into the skin sac at birth, but stay in the abdomen, where the temperature is much higher. As a result, tumors of various etiologies appear.
Factors that cause tumors:
- genetic susceptibility;
- testicular injury;
- testicular hypoplasia;
- surgical intervention;
- Can't get pregnant.
If you've been diagnosed with a malignant tumor, don't despair. Testicular cancer detected early can be cured very effectively. Therefore, it is very important to consult your doctor immediately if you experience any pain.
Testicular injuries: causes and diagnosis in men and children
When the testicles are injured, the cause in men can be caused by a variety of conditions typical of adults, but in children the cause tends to be simpler.
Almost all pain that occurs is caused by trauma or wearing tight underwear. In addition to pain, there is abrasion and irritation of the skin's surface, often swelling.
Bruised testicles most often occur during active and highly mobile play, or during childish fights where the child is shot in the scrotum. Bruising can also occur while riding a vehicle such as a bicycle (failed landing on a hard seat). On impact, there is pain, damage to the inner shell of the testicle, and swelling. The scrotum turns purple.
Twist around the axis. In normal health, the testicles are attached to the "outside" of the scrotum by so-called strands. In boys, it sometimes occurs that the fastening is weaker and therefore twisting occurs. The blood vessels themselves twist, which is why blood flow is disturbed at first, and then may stop completely.
There is severe pain, swelling of the testicles, and pain to the touch. This condition is accompanied by nausea and severe vomiting and requires surgical intervention. In older boys, the vas deferens, which lie on either side of the testicles, may also be damaged.
The testicles are swollen, and the scrotum is red and swollen on one side, and is painful to palpation. Mumps, in mumps in the common man, causes inflammation of the testicles as a complication. After treatment with multiple hormones, the risk of infertility is significantly reduced. Other disorders - edema, inguinal hernia, testicular hypoplasia, absence of a single testicle in the scrotum. Sometimes young parents think their child has no testicles.
They're definitely there, they're just not where they should be, which is to say, not in the right place, not in the scrotum. During fetal development, the testes are located near the kidneys. As the fetus grows and develops, they descend, and almost before birth, they descend into the scrotum. Sometimes the testicles do not descend. This phenomenon is called cryptorchidism.
The disease does not cause any inconvenience or acute discomfort, but men who have reached adulthood due to the disease can suffer from a dreaded disease like infertility. So surgery was performed (until the child was six years old) - the testicles were lowered into the scrotum.
When the testis remains in the abdominal cavity, there may be a tumor there. What to do to avoid irreversible consequences. How to deal with the problem? What is the solution to testicular pain? The cause in men and children has been identified, and now we need to figure out how to treat it. Initially, you should contact a highly specialized doctor and go through a series of procedures for a diagnosis.
The doctor examines the patient, asks, and sends it to the lab to check:
- donate blood.
- Urine was given.
- If there is discharge from the glans, a urethral swab is done.
- Mandatory ultrasonography of the testis.
A doctor will prescribe treatment based on the cause of the pain.
Treatment of minor injuries and bruises is done at home under the supervision of a doctor and includes:
- Take anti-inflammatory drugs, anesthesia.
- The scrotum is elevated.
- Apply ice to the injured area.
- If the scrotum is torn due to a bruise, blood can build up inside, making it impossible to treat without prompt surgical intervention.
Epididymitis. In most cases, outpatient treatment is performed, but if the situation is particularly neglected and difficult, then inpatient treatment is essential.
treat:
- Antibiotics for 14 days of reception.
- Take medicines that reduce inflammation.
- Take medicine to relieve pain.
- Perform scrotal support.
- If complications arise, there is no way to do it without surgery. What complications are we talking about? Especially about scrotal abscesses.
Inguinal hernias are treated only with surgery.
Treatment is done on an outpatient basis if the patient agrees, but at the same time must be surgically corrected for the hernia, which was strangled and caused pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
Regardless of the cause, testicular pain is caused, so treatment is prescribed and under strict medical supervision and supervision. You shouldn't be left alone because the consequences are irreversible and a person loses their normal sex life and the chance to become a parent and continue their race because of stupidity. All diseases can be avoided.
For this, don't forget personal hygiene and follow simple rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- Eat a reasonable diet and follow the rules;
- Be selective in sexual relationships and don't forget to protect yourself;
- Regular sex is also a way to prevent cancer.
Check the testicles yourself more often. You can do this in the tub as your skin relaxes from the warm water. With the pouch in the palm of your hand, one testicle may be slightly larger, but the weight should be the same. Roll your testicles with your fingers and feel it. Check their seals. Healthy testicles are oval in shape, not hard, smooth to the touch, and free of lumps.
Do this with both testicles. Check the spermatic cord carefully. They should be smooth and elastic. Also examine both testicles. Examine the appendages at the back of the testicles. Small bumps should be soft and supple. If the disease still strikes you, don't despair and don't panic. The most important thing is to establish the correct diagnosis.